Network management refers to a network’s administration, maintenance, and oversight, covering both hardware and software.
Contents
Hyperscale is a term used to describe the ability to scale up network resources like memory or CPU on demand and without limits. Businesses with quickly changing workloads or vast data storage and processing needs may consider adopting a hyperscale approach, purchasing space in a specialized hyperscale data center that can accommodate these needs.
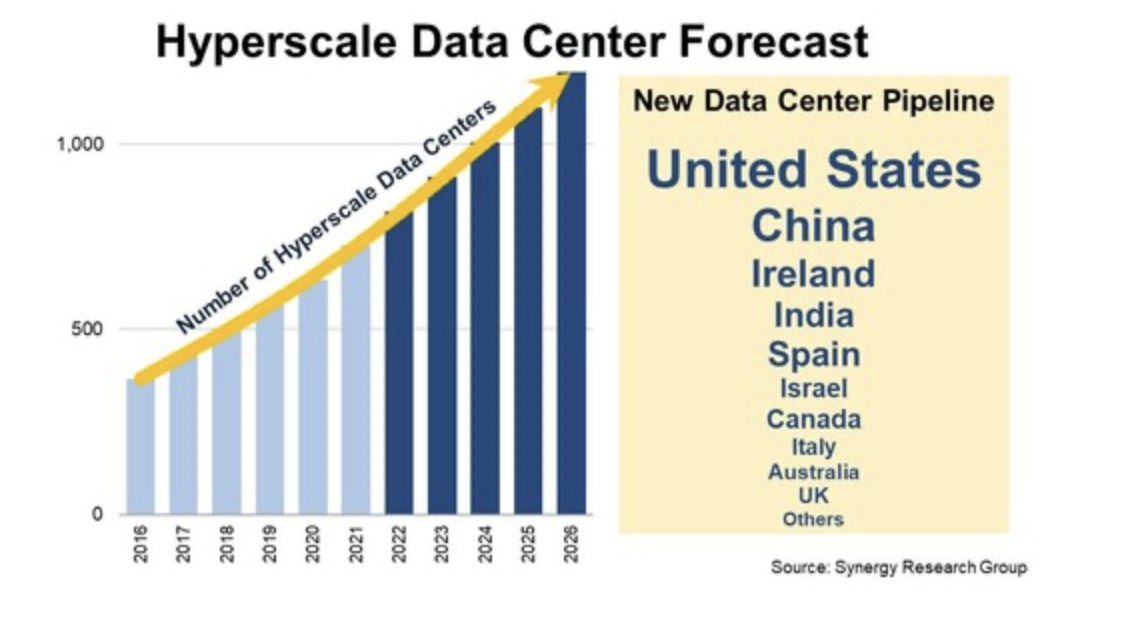
According to a 2021 study by the Synergy Research Group, the U.S. is leading the trend in adoption, accounting for 49% of the capacity in hyperscale datacenters.
Organizations that adopt the hyperscale model are sometimes referred to as hyperscalers. Examples include IBM, Microsoft, Apple, Amazon, Facebook, Alibaba, and Google. They often own a significant market share in the hyperscale data center space, building private facilities for their own needs.
How Does Hyperscaling Work?
Hyperscale computing occurs in data centers over modular IT infrastructure. It uses a modular architecture that is more energy efficient and easier to expand than traditional data center infrastructure. Modular IT infrastructure is made up of thousands of compressed, minimalistic servers networked together horizontally on multicore processors.
Size is what makes hyperscale efficient and readily available. These environments have displaced more traditional enterprise-level data centers and are at least 5 – 10 thousand square feet (typically larger). Facebook’s nine hyperscale data centers in Prineville, Oregon, collectively have over 4.6 million square feet of capacity.
Companies may adopt hyperscale computing as the most efficient way to address high-volume “big data” analytics projects requiring high-density computing power and availability.
Examples of projects that use hyperscale computing to address significant data initiatives include
- Amazon’s ultra-targeted ad campaigns to end-users
- Organizations analyzing cyberattack events to create predictive models
- Government disaster and rescue responses efforts that use big data to better target and predict event impacts
- Running Google Analytics
- GPS tracking of packages in real time
- Uber adjusts driving prices based on anticipated demand spikes and driver availability.
Gartner predicts that by 2025, 80% of enterprises will have shut down their traditional data center.
Challenges with Adopting Hyperscale Approach
Hyperscale computing can come with significant network visibility and performance management challenges. Network engineers need to see into the architecture of these physical and virtual environments, and the leaf-spine switching model found in hyperscale computing is incredibly complex.
Hyperscalers must incorporate network topography tools that reveal real-time bidirectional traffic flows (east-west and north-south), path congestion, and the status of data center interconnects.
These tools need to see performance metrics from the inside and the application dependencies and resource allocation outside the data center. For successful hyperscale deployments, IT Teams need to prioritize visibility tools in their stack that can monitor performance metrics within the hyperscale environment.
Hyperscale Visibility Challenges
While you can analyze hardware-centric data center operations with packet capture (PCAP) solutions, the shift to virtual components creates major network blind spots. With the increasingly popular network function virtualization (NFV), this software-based routing is removed from machines and devices, eliminating the packet capture solution. Without visibility into traffic and devices, the benefits of the hyperscale solution are lost on troubleshooting delays from unchecked bottlenecks and unidentifiable network events.
How to Address Virtual Blindspots in Hyperscale Data Centers
LiveAction’s monitoring platform uses LiveNX to gain visibility into virtual network traffic with both east-west and north-south direction monitoring. LiveWire Virtual can be deployed in virtual environments to capture packets and generate flow from virtual routers and switches. These virtual routers and switches produce flow that our LiveNX flow collector can analyze. Additionally, LiveAction converts VPC logs into flow that LiveNX also ingests.
Don’t let visibility get in the way of hyperscaling plans.
About LiveAction
Hyperscaling is the way of the future. It’s critical to have network monitoring tools that don’t create obstacles for your growth initiatives. LiveAction technology is built with the future in mind. Get complete visibility into network and application performance across multi-vendor, multi-domain, and multi-cloud networked environments. LiveAction provides the broadest telemetry available on the market for an enhanced understanding of network security and performance from just one platform.
Want to learn more? Talk to an expert today.
