Let’s first consider how SD-WAN works to understand where visibility gaps naturally occur. SD-WAN is a software-based intelligent network layer. It can classify, select, and switch traffic paths across your WAN depending on network saturation and QoS policies. This reactive rerouting and load balancing to adjust for network congestion help improve network availability and performance levels across an organization.
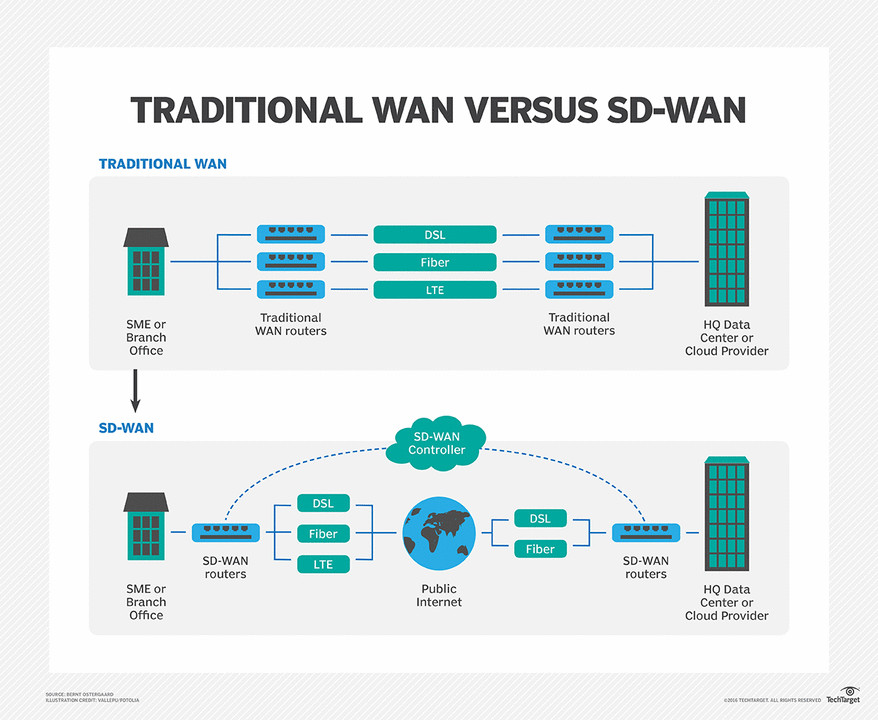
The SD-WAN architecture allows direct access to cloud resources saving time and bandwidth compared to the traditional hub and spoke model. In a traditional model, traffic has to be backhauled to a central data center (the hub) for processing, clogging internet lines and increasing latency. As traffic and data have increased year over year, this architecture was no longer meeting the needs of many organizations.
The SD-WAN model improves network performance through its direct path model that routes bandwidth over the best path and transport type depending on traffic levels. But for any of these benefits to occur, organizations need visibility in these three areas of their SD-WAN.
1 – Application Visibility
For SDWAN to make the correct provisioning and routing decisions, visibility into application performance is required. SD-WAN enforces the right QoS policy based on how an application is tagged. Network and application monitoring is needed to understand how to prioritize and classify applications.
With visibility into an application’s QoS priority, the SD-WAN network can select the best traffic paths that use the least expensive bandwidth while maintaining network performance. For example, you may opt to go with a broadband link for an application with a lower priority and an ethernet link for an application of higher priority.
Monitoring tools can deliver insights on applications like response times, performance, and bandwidth usage to determine what prioritization they need within QoS policies. This application grouping allows for the most efficient resource allocation, ensuring the performance of critical applications during peak traffic. Visibility into the performance metrics of applications is critical to setting sound policies.
Like the saying “Garbage in Garbage out,” the SD-WAN can only work off the policies given to respond to traffic.
2 – Underlay Visibility
There is often a gap in visibility between the tunnels riding over the network and the underlying transport network, and SD-WAN visibility leans heavily on the virtual overlay. The underlay network is a hardware-dependent physical network responsible for delivering packets. The underlay network can be internet, MPLS, satellite, Ethernet, broadband, or any transport mode. The overlay is a virtual network that is transport agnostic and uses tunnel encapsulations like IPSec, GRE, or VXLAN. The overlay is easy to scale, segregates applications by class of service (CoS), and supports multi-path forwarding.
Visibility challenges in the SD-WAN’s underlay transport network can slow troubleshooting and threat identification. Without visibility into the underlay connection, you are left at the mercy of the ISP, waiting in a queue for resolution or blindly increasing bandwidth without knowing if it will solve the root issue.
It’s imperative to select a monitoring solution that can visually unite and monitor the underlay and overlay layers of an SD-WAN network. Our flow collector, LiveNX supports and correlates SD-WAN data into topology mapping, reporting, and alerting. Having topographically representing traffic flow on all network transport links allows for split-second response times. This visualization also provides insights into network trends and patterns for better-informed policies and routing decisions.
Related Assets

3 – Security Visibility
Security visibility needs to cover the underlay and overlay of the SD-WAN network, considering devices, domains, IPs, users, and connections throughout the network.
Often, malicious traffic can hide out in encrypted packets. Deep packet dynamics (DPD) combined with AI can fingerprint the metadata of the packet and use behavioral heuristics to see through encrypted traffic for threats without needing decryption. This saves significant network resources and avoids decrypting potentially protected PII data.
Encryption law is unclear about the competing interests in protecting the public by decrypting suspicious traffic ( classified in some cases like search and seizure) vs. the constitutional protections against self-incrimination through this decryption. Texas has a law on Unlawful Decryption, and it’s uncertain if this decryption anxiety will spread.
Conclusion
Backed by adequate visibility, SD-WAN can improve network performance, support increased traffic, and make better use of resource allocation.
But without visibility into the three areas discussed you are left with some serious problems:
- Poorly designed QoS policies
- High-security risk levels from encrypted traffic
- Chaotic troubleshooting of underlay network
Finding a vendor-agnostic monitoring platform with tools that bring visibility into every layer of the network ensures that your deployment is a success and that ongoing SD-WAN stability is achievable.
Read more about how LiveAction’s SD-WAN monitoring solution can bring visibility to SD-WAN deployments over hybrid physical and virtual appliances. Or see it in action. Schedule your demo today.



